Best Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber Techniques for Precision?
In the realm of precision manufacturing, "Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber" has gained significant traction. Experts emphasize the importance of mastering techniques in this field. Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned specialist in laser applications, once stated, “Precision is the key to unlocking the full potential of silicone rubber.” This highlights the significance of skilled methods in achieving desired outcomes.
The process of Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber demands advanced knowledge and attention to detail. Many face challenges with material thickness and cutting speed. The wrong settings can lead to uneven edges or excessive heat, damaging the material. Understanding the right balance is crucial for quality results.
Furthermore, the industry has seen rapid advancements, yet there are still areas needing improvement. Many practitioners rely on trial and error. This prolongs the learning curve. By focusing on best practices, we can enhance the efficiency of Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber. Embracing these techniques can pave the way for innovation and accuracy in the manufacturing process.

Understanding Silicone Rubber and Its Applications in Laser Cutting
Silicone rubber is a versatile material widely used in various industries. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist chemicals makes it ideal for many applications. In laser cutting, understanding the unique properties of silicone rubber is crucial. The material can be tough to cut due to its elasticity and thickness. Proper techniques can enhance precision when using lasers.
When cutting silicone rubber, the right settings are essential. Adjusting the laser's power and speed can yield better results. Lowering the speed reduces the chance of burning the edges. However, cutting too slowly may result in material distortion. Experimentation is key to finding the optimal balance. Maintaining cleanliness around the cutting area is also critical. Excess dust or debris can affect the cut quality.
Precision in laser cutting silicone rubber often requires reflection on techniques. Sometimes, the cut edges may not be as smooth as expected. Learning from these outcomes can lead to improved methods. Regular maintenance of the laser equipment can prevent inconsistencies. Consideration of the material's properties and shared experiences can enhance cutting techniques.
Best Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber Techniques for Precision
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutting | Utilizes a carbon dioxide laser beam to cut through materials. | High precision and clean cuts with minimal post-processing. | Gaskets, seals, and intricate designs in various industries. |
| Fiber Laser Cutting | Employs fiber optics to generate a high-intensity laser beam. | Faster cutting speeds and lower operation costs. | Automotive parts, medical devices, and custom prototypes. |
| Edge Sealing | Seals the edges of rubber while cutting to prevent fraying. | Enhances durability and appearance of finished products. | Consumer goods and specialized packaging applications. |
| Multi-Layer Cutting | Allows simultaneous cutting of multiple silicone rubber layers. | Increases production efficiency and reduces material waste. | Complex assemblies and layered seals in electronic industries. |
Essential Laser Cutting Equipment for Working with Silicone Rubber
When working with silicone rubber, the right equipment is essential for achieving precision. A CO2 laser cutter is often preferred due to its ability to handle various thicknesses effectively. The selection of lens and mirrors impacts the cutting quality. A high-quality lens will provide a clean cut, minimizing residue.
Tips: Regularly check your equipment for wear and tear. This can save you from unexpected downtime. Also, experiment with different settings on your laser cutter. Finding the perfect balance may require adjustments, so don’t hesitate to take notes on your results.
Another key piece of equipment is a reliable ventilation system. Fumes can be hazardous when cutting silicone. Good ventilation minimizes risks and keeps your workspace safe. Pay attention to the materials you’re using. Different silicone types react differently to lasers. Be prepared to make minor tweaks for best outcomes.
Tips: Always prioritize safety gear. Protective eyewear and masks should be mandatory. As you progress, document the techniques that work best for you. This can serve as a valuable resource for future projects.
Best Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber Techniques for Precision
Techniques for Achieving High Precision in Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber

Laser cutting silicone rubber requires careful techniques to achieve precision. The material is thick and can be challenging to manipulate. Using high-quality lasers can make a difference. A focused beam ensures clean edges and reduces jagged cuts. However, each setup requires experimentation. Adjusting the laser's speed and power is crucial. Too high a speed may cause improper cuts. Conversely, too low a speed can result in burns.
Temperature control is another vital factor. Keeping the rubber cool prevents it from melting or warping. A cooling system can enhance the cutting process. Also, using the right nozzle size helps. A larger nozzle may not provide the detail needed for intricate designs. It’s essential to test multiple configurations before finalizing a design. Each adjustment can lead to noticeable differences in the final product.
Finally, proper file preparation is necessary. High-resolution vector files work best for laser cutting. They ensure that the cutting path is accurate, yet this doesn’t eliminate the potential for errors. Sometimes, despite thorough planning, unexpected results occur. It’s important to evaluate each attempt and refine techniques. This reflective practice can lead to improvements over time.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Laser Cutting Silicone Rubber
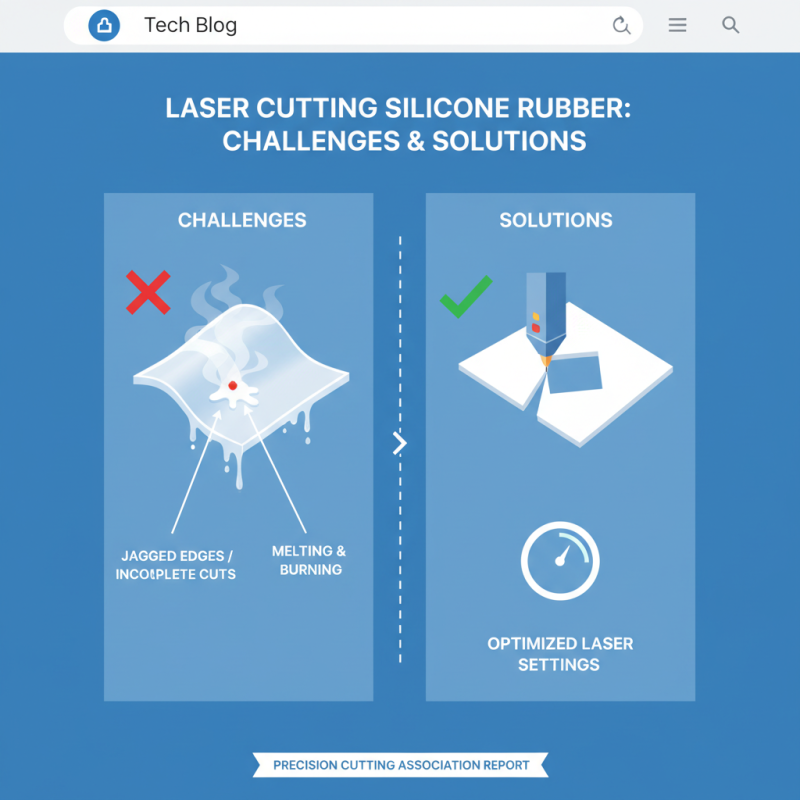
Laser cutting silicone rubber can be tricky. While it's a popular technique for creating precise shapes, there are challenges to overcome. One common issue is the material's tendency to melt. When exposed to high heat, silicone can burn instead of cut cleanly. This often leads to jagged edges or incomplete cuts. According to a technical report by the Precision Cutting Association, optimizing laser settings can reduce these problems significantly.
With experimentation, many operators have found effective techniques. Maintaining lower power settings helps avoid thermal damage. A slower cutting speed can enhance precision while minimizing the risk of burns. Using a focused beam is essential. It ensures that the cut remains clean and sharp.
Tips: Always test your settings on scrap material first. This practice will help you gauge the necessary adjustments. Keep your equipment well-maintained to avoid inconsistencies in cutting. Remember that minor variations in speed or power can make a big difference.
Another challenge is the tendency for silicone to warp during cutting. Some users report a lack of control over the material. This can lead to unwanted deformations. Implementing a vacuum table can help hold the material securely.
Tips: Use heavier weights for larger sheets to maintain flatness. Adjusting the focal point of the laser also aids precision. Regular checks on the machine's alignment can prevent common issues.
Best Practices for Maintaining Quality and Consistency in Laser Cutting
Laser cutting silicone rubber requires precision and care. To maintain quality and consistency in your projects, following best practices is crucial. According to industry reports, ensuring correct settings for speed and power can significantly impact cut quality. Deviating even slightly can compromise the integrity of the material, leading to frayed edges or incomplete cuts.
Tip: Always perform a test cut on scrap material before commencing with the actual project. This ensures that you can adjust the settings based on the rubber thickness and type. Casual errors can result in wastage and increased costs.
Another vital aspect is regular maintenance of the laser cutting equipment. Accumulated residue from previous cuts can lead to inconsistent performance. Studies indicate that proper cleaning can improve cutting efficiency by up to 20%. Always inspect lenses and mirrors for any signs of wear or damage.
Tip: Schedule routine maintenance checks. Keeping the machinery in optimal condition minimizes downtime and enhances output quality. Reflect on the mistakes, and learn from inconsistent cuts. Understanding these aspects is key to perfecting silicone rubber cutting.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Innovative Alternatives to Laser Cutting Rubber for Global Suppliers
-

5 Amazing Benefits of Synthetic Rubber You Need to Know
-

How to Select the Best Natural Gum Rubber for Your Sustainable Products
-

Innovative Solutions for Molding Rubber Applications in Global Manufacturing
-

Unlocking the Benefits of Polyisoprene Rubber: Why It's the Future of Sustainable Materials
-

Exploring Sustainable Alternatives to Best Natural Gum Rubber for Global Buyers