How to Effectively Vulcanize Rubber for Optimal Performance and Durability
Vulcanizing rubber is a crucial process in the production of durable and high-performance rubber products, with applications spanning various industries including automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing. According to the International Rubber Study Group, the global demand for rubber is projected to reach 30 million tons by 2025, indicating the increasing reliance on effective vulcanization techniques to enhance the longevity and functionality of rubber materials. The vulcanization process involves the cross-linking of polymer chains through heat and chemical additives, which not only improves the rubber’s elasticity but also its resistance to environmental factors such as heat, moisture, and oxidation.
In order to achieve optimal performance and durability, the specific parameters of vulcanizing rubber must be meticulously controlled. Reports from the American Chemical Society have indicated that variations in temperature, time, and the choice of vulcanizing agents can significantly impact the mechanical properties of the rubber. Proper vulcanization not only increases the lifespan of rubber products but also reduces the risk of failure in high-stress applications. This underscores the importance of understanding the vulcanization process, as it directly correlates with the performance standards expected in modern industrial and consumer applications. Consequently, mastering the techniques of vulcanizing rubber is essential for manufacturers aiming to meet quality benchmarks and drive innovation in rubber product performance.

Understanding Vulcanization: Definition and Importance in Rubber Production
Vulcanization is a crucial chemical process in the production of rubber, where raw rubber is transformed into a more durable and elastic material. This transformation is primarily achieved by the introduction of sulfur or other vulcanizing agents that create cross-links between the individual polymer chains. These cross-links increase the strength and resilience of rubber, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from tires to industrial machinery.
The importance of vulcanization in rubber production cannot be overstated. Without this process, rubber would remain a soft and sticky material with limited usability and lifespan. Vulcanization enhances several key properties including elasticity, heat resistance, and overall durability. As a result, products made from vulcanized rubber can withstand significant wear and tear, making them ideal for demanding environments. This process also ensures that the rubber maintains its performance characteristics under varying conditions, thus extending its service life and improving reliability in its applications.
Key Materials Used in the Vulcanization Process for Rubber
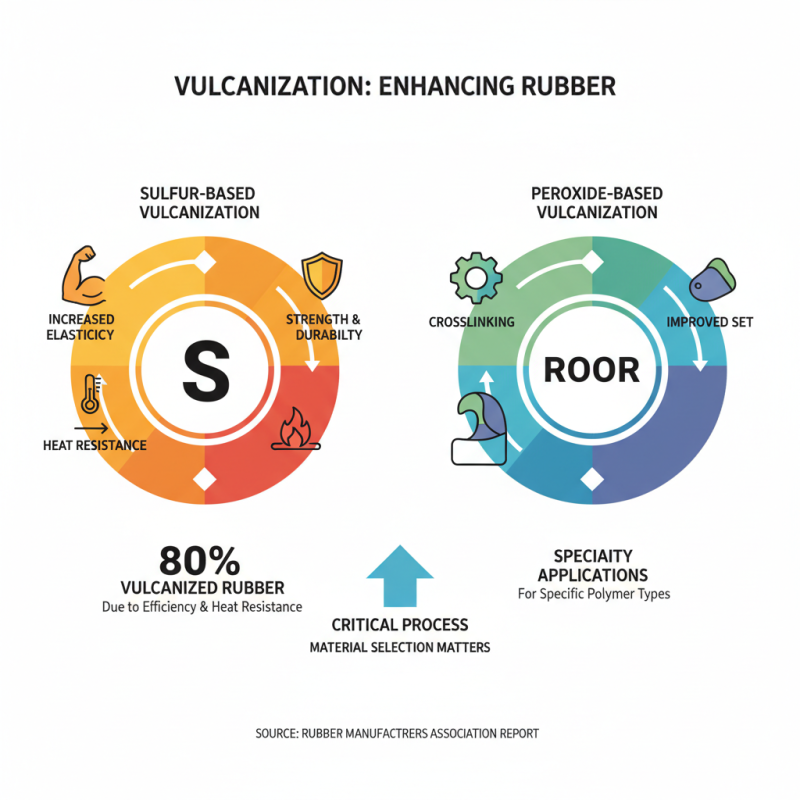
Vulcanization is a critical process in rubber manufacturing that enhances the material's elasticity, strength, and durability. A key aspect of this process lies in the selection of appropriate materials, which can significantly impact the final product's performance. The two most common types of vulcanization agents are sulfur and peroxides. According to a report by the Rubber Manufacturers Association, about 80% of vulcanized rubber utilizes sulfur due to its efficiency in cross-linking rubber molecules and improving heat resistance.
In addition to vulcanizing agents, accelerators play a vital role in speeding up the vulcanization process. Commonly used accelerators include dibenzothiazole disulfide (MBTS) and sulfenamides, which have been shown to enhance the rate of cross-link formation. A study from the International Journal of Polymer Science noted that the right choice of accelerator can reduce processing time by up to 30%, leading to increased productivity and lower manufacturing costs.
**Tip:** When selecting vulcanization materials, it is crucial to consider the intended application of the rubber product. For example, rubber intended for high-stress environments may require a balance of strength and flexibility achieved through the right combination of sulfur and accelerators. Regularly consulting industry reports can help stay informed about advancements in vulcanization techniques and material innovations.
Another essential component in the vulcanization process is fillers, such as carbon black, which enhance mechanical properties and reduce costs. According to a market analysis by Grand View Research, the demand for carbon black in rubber applications is projected to reach over 14 million tons by 2025, emphasizing its importance in the industry. Understanding the compatibility and proportions of these fillers can lead to better performance and durability outcomes in the final rubber product.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Vulcanization Process for Optimal Results
Vulcanization is critical in enhancing the performance and durability of rubber products, making it essential to follow a methodical process for achieving the best results. The traditional vulcanization process involves heating rubber with sulfur, which forms cross-links between polymer chains, providing the material with increased resilience and elasticity. According to the American Chemical Society, the optimal temperature range for vulcanization is typically between 140-160°C, ensuring that the chemical reactions occur efficiently without degrading the rubber.
To achieve optimal results, it's crucial to control several parameters during the vulcanization process. First, the mixing of ingredients—including sulfur, accelerators, and fillers—must be precise. Studies published in the Journal of Applied Polymer Science indicate that improper mixing can lead to inconsistencies in rubber properties, affecting its strength and durability. Furthermore, the duration of the vulcanization process is equally important; too short a time may lead to incomplete curing, while excessive time can degrade the rubber.
Researchers recommend monitoring the viscosity and temperature throughout the process to ensure that the rubber reaches the desired state of elasticity and toughness.
By systematically controlling these variables, manufacturers can produce high-quality rubber products that meet industry standards for performance. The use of advanced technologies, such as dynamic mechanical analysis, helps in fine-tuning the vulcanization process, aligning with data from the Rubber Industry Association that emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement in manufacturing practices to enhance product lifecycle and sustainability.
Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of Rubber Vulcanization
Vulcanization is a crucial process in rubber production that enhances its performance and durability, but several factors can significantly influence its effectiveness. One primary factor is the type and amount of sulfur used in the vulcanization process. According to a study by the Rubber Research Institute, the optimal sulfur content typically ranges between 1.5% to 2.5% of the total rubber weight. Excessive sulfur can lead to over-vulcanization, causing brittleness, while insufficient sulfur results in under-vulcanized rubber that lacks elasticity and strength.
Another critical factor is the vulcanization temperature and time. Research indicates that a temperature range of 140°C to 180°C is most effective for achieving the desired cross-link density. The curing time also plays a vital role; studies have shown that curing for too short a duration can leave the rubber inadequately vulcanized, while excessive curing leads to degradation of the polymer matrix. The ideal curing time can vary based on the thickness of the rubber product and the specific formulation, which necessitates careful monitoring and adjustments during the manufacturing process.
The presence of accelerators can also affect vulcanization efficiency. The choice of accelerator type and concentration can enhance the speed of the vulcanization reaction, thereby reducing cycle times and energy consumption in production. Industry data suggests that using the right combination of accelerators can improve the tensile strength of the final rubber product by up to 30%, making this an essential consideration for manufacturers seeking optimal performance. Understanding and controlling these factors are vital for achieving high-quality vulcanized rubber that meets demanding performance and durability standards.
Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of Rubber Vulcanization
Testing and Quality Control Methods for Vulcanized Rubber Products
Testing and quality control play a crucial role in the production of vulcanized rubber, ensuring that the final products meet stringent performance and durability standards. According to a report by the Rubber Manufacturers Association, approximately 75% of defects in rubber products can be traced back to inadequate testing methods during production. This underscores the importance of implementing a systematic approach to quality control. Key testing methodologies include tensile strength tests, elongation at break, and compression set tests, which help manufacturers assess the mechanical properties and functional longevity of their rubber products.
Furthermore, advancements in non-destructive testing techniques, such as ultrasonic testing and thermal imaging, have revolutionized the monitoring of vulcanization processes. A study published in the Journal of Rubber Research highlighted that utilizing these modern techniques can reduce defect rates by up to 50%, significantly enhancing product reliability. Additionally, adherence to industry-specific standards, such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials, ensures consistency and facilitates international trade, offering manufacturers a competitive edge in the global market. Maintaining rigorous testing and quality control protocols not only enhances product performance but also builds consumer trust in vulcanized rubber products.
Related Posts
-

Advantages of Utilizing Rubber Processing Techniques for Global Trade
-

How to Source the Best Vulcanizing Rubber for Your Production Needs
-

Exploring Thermoplastic Rubber Innovations at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Unlocking the Benefits of Polyisoprene Rubber: Why It's the Future of Sustainable Materials
-

Mastering Ultrasonic Welding Rubber: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
-

5 Amazing Benefits of Synthetic Rubber You Need to Know