What is Rubber Processing? Understanding Techniques and Applications
Rubber processing is a crucial aspect of the rubber industry that involves transforming raw rubber into useful products through various techniques and applications. According to the Rubber Statistical Yearbook published by the International Rubber Study Group, the global consumption of natural rubber surpassed 13 million tonnes in recent years, highlighting the significant role rubber has in a variety of industries, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods. The growing demand for rubber products can be attributed to its unmatched elasticity, durability, and versatility, making rubber processing an essential field of study and practice.
The techniques employed in rubber processing, such as mixing, molding, extrusion, and vulcanization, are vital for enhancing the material's properties and achieving desired specifications. The European Rubber Journal notes that advancements in processing technologies have led to improved efficiency and reduced waste, contributing to the sustainability goals within the industry. As market dynamics evolve, understanding these processes and their applications is fundamental for industry professionals and researchers alike to adapt to current trends and innovations. In this context, rubber processing not only represents a key industrial function but also a gateway to innovative solutions in material development and product manufacturing.

Introduction to Rubber Processing and Its Importance
Rubber processing is a vital part of numerous industries, significantly influencing the performance and durability of many everyday products. The global rubber processing market is projected to reach approximately $6.4 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for rubber products across automotive, construction, and consumer goods sectors. Understanding the techniques and applications of rubber processing is crucial for professionals involved in materials science and manufacturing, as it directly impacts product quality and efficiency.
One of the most essential aspects of rubber processing is the ability to enhance the physical and chemical properties of rubber. Techniques such as vulcanization and compounding allow manufacturers to tailor rubber for specific applications, whether it’s the flexibility needed for high-performance tires or the durability required for industrial seals. According to a report by Smithers, the global demand for engineered rubber products is expected to grow at a rate of approximately 4.5% annually over the next five years. This growth underscores the importance of innovative processing techniques that can meet the evolving requirements of various applications while minimizing environmental impacts.
In addition to improving product characteristics, effective rubber processing methods contribute to waste reduction and sustainability in manufacturing processes. As industries move towards greener practices, advancements in rubber recycling and waste management are becoming increasingly significant. For example, the global recycled rubber market is estimated to reach $10 billion by 2027, showcasing the growing importance of sustainable practices in rubber processing. The ongoing research and development in this area are key to ensuring that rubber products continue to meet consumer demands while adhering to environmental responsibilities.
Overview of Rubber Processing Techniques and Methods
Rubber processing involves a series of techniques and methods that transform raw rubber into usable products. One fundamental technique is the mastication process, which involves breaking down the rubber's molecular structure to improve its flow characteristics. This is typically done using an industrial machine called a rubber mill, where rubber is subjected to mechanical stress and heat. This process enhances the plasticity of the rubber, making it easier to mold and shape into various forms.
Another critical method in rubber processing is vulcanization, which is a chemical process that involves adding sulfur to the rubber compound. This step is essential as it improves the elasticity, durability, and overall strength of the rubber products. By creating cross-links between the rubber molecules, vulcanization ensures that the material can withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. Additional techniques such as extrusion and molding further refine the processing of rubber, enabling manufacturers to produce a wide range of items, from tires to seals and hoses, catering to various industries. Each processing technique is crucial in determining the final properties of the rubber products, ultimately influencing their performance in real-world applications.
What is Rubber Processing? Understanding Techniques and Applications
| Processing Technique | Description | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoforming | A process that uses heat to soften rubber, allowing it to be molded into specific shapes. | Automotive parts, seals, and gaskets. | High precision and low waste. | Limited to simple shapes. |
| Extrusion | A continuous process of shaping rubber by forcing it through a die. | Rubber hoses, tubing, and profiles. | Efficient for long lengths and complex profiles. | Initial setup can be costly. |
| Calendering | A process where rubber is passed through rollers to produce thin sheets. | Rubber sheets for flooring and conveyor belts. | Ability to produce large surfaces. | Labor-intensive process. |
| Injection Molding | A process that injects molten rubber into a mold to create specific shapes. | Various industrial parts and consumer products. | High efficiency and low per-item cost for large runs. | High initial mold cost. |
| Compression Molding | A method that compresses rubber in a mold to form products. | Bumpers, gaskets, and other components. | Simple setup for quick production runs. | Longer cycle times compared to other methods. |
Mechanical Processing: Extrusion, Molding, and Calendaring
Mechanical processing of rubber includes essential techniques such as extrusion, molding, and calendaring, each serving specific applications in the production of rubber products. Extrusion involves forcing rubber through a shaped die to create continuous profiles, such as hoses, seals, and gaskets. This technique offers precision in form and size, allowing manufacturers to produce long lengths of rubber components efficiently. The process can be adjusted for various thicknesses and shapes, making it versatile for diverse industrial applications.
Molding, on the other hand, involves shaping rubber by enclosing it within a mold cavity. This technique can be used for creating intricate shapes and parts, such as automotive components and consumer goods. There are various molding methods, including compression and injection molding, each suited for different production scales and complexities. Injection molding, in particular, provides an excellent finish and precise dimensions, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Calendaring is another significant mechanical processing method where rubber is passed through a series of rollers to achieve desired thickness and surface finish. This technique is crucial for producing sheets of rubber that can be further processed or used in applications like tire manufacturing and flooring materials. The controlled environment and pressure of calendaring allow for uniformity in thickness and texture, catering to specific performance requirements in different applications. Together, these mechanical processing techniques form the backbone of rubber production, enabling the creation of a wide array of products that meet various industrial needs.
Rubber Processing Techniques Overview
Chemical Processing: Vulcanization and Additive Application

Vulcanization is a critical chemical processing technique in rubber manufacturing that significantly improves the elasticity, strength, and durability of rubber products. Through the application of heat and sulfur, this process creates cross-links between polymer chains, transforming natural or synthetic rubber into a more resilient material. According to a report by Global Market Insights, the global rubber processing market is projected to exceed $100 billion by 2026, highlighting the essential role that vulcanization plays in meeting industrial demands.
The incorporation of various additives during the rubber processing phase further enhances the performance and longevity of rubber products. Common additives include accelerators, fillers, and antioxidants, each serving specific functions that optimize the rubber's properties. For instance, carbon black is widely used as a reinforcing filler and can increase the tensile strength of rubber by up to 70%. The innovative use of these additives can lead to advancements in applications ranging from automotive tires to industrial seals, underpinning a market that the Smithers Group estimates will grow at a CAGR of 3.2% over the next five years. Understanding the intricacies of chemical processing in rubber production is vital for manufacturers aiming to innovate and meet the evolving demands of various industries.
Applications of Processed Rubber in Various Industries
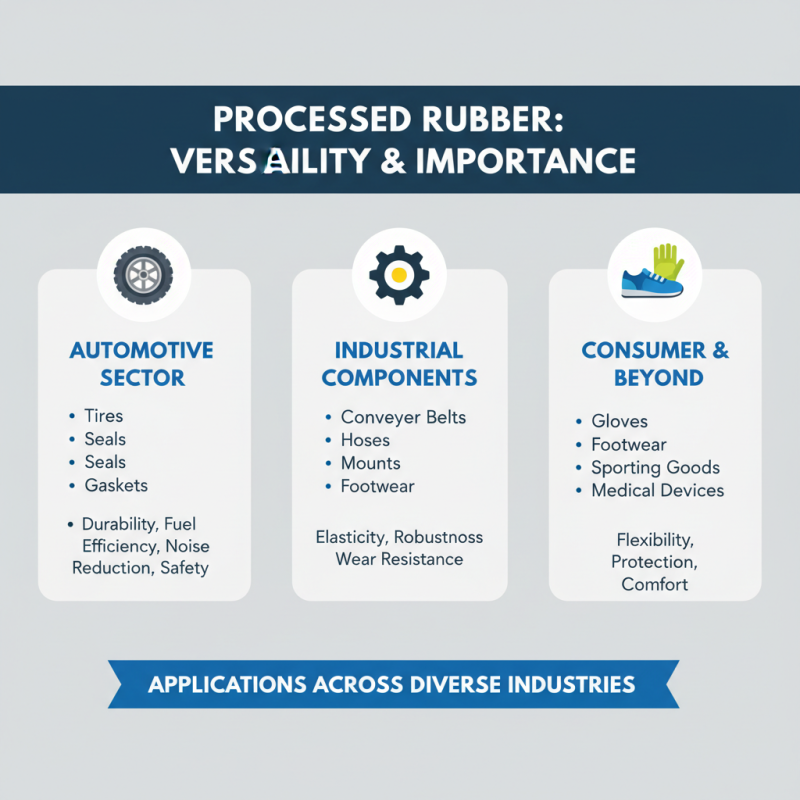
Processed rubber has a wide range of applications across various industries, highlighting its versatility and importance. In the automotive sector, for instance, processed rubber is crucial for manufacturing tires, seals, and gaskets, which enhance performance and ensure safety. These components not only provide durability but also improve fuel efficiency and reduce noise. The elasticity and robustness of rubber make it an ideal material for items that undergo significant wear and tear.
In the construction industry, processed rubber is utilized in the production of flooring materials, sealants, and insulation. Rubber flooring offers excellent shock absorption and slip resistance, making it perfect for gyms, playgrounds, and hospitals. Additionally, rubberized asphalt is gaining popularity in road construction, providing superior weather resistance and longevity compared to traditional materials.
Tips: When working with processed rubber, consider the environment in which it will be used. For outdoor applications, select rubber compounds that are resistant to UV rays and weathering. In indoor settings, choose options that prioritize safety, such as slip-resistant surfaces for high-traffic areas. Understanding these details can significantly enhance the performance and lifespan of rubber products in various applications.
Related Posts
-

Advantages of Utilizing Rubber Processing Techniques for Global Trade
-

Global Leaders in Best Rubber Processing Proudly Manufacturing in China for the World
-

Elevating Global Standards with China's Premier High Cis Polybutadiene Solutions
-

China's Resilience in Manufacturing Best Ultrasonic Welding Rubber Amidst US China Tariff Challenges
-

5 Key Reasons to Choose Brominated Butyl Rubber for Your Next Project
-

Tpr Rubber Market Insights and Trends for Global Buyers in 2025